| |
Abstract
Hybrid cloud combines private resources with public paid resources from cloud service providers. This combination creates challenges for scheduling tasks due to the heterogeneous nature of resources, and the different features of the private cloud from the public, so that scheduling is carried out according to quality-of-service constrains, the most important of which is cost and deadline.
This paper presents a new algorithm for task scheduling for the hybrid cloud named HGTH (Hybrid Genetic algorithm for Task scheduling in Hybrid cloud), which combines heuristics and meta-heuristics The proposed algorithm applies a genetic algorithm to the workflow by making use of the heuristic E-HEFT algorithm at the initial stage of tasks allocation to the available resources, so that the low-cost resources are given higher priority, taking into account the deadline.
The practical study of the research showed the efficiency of the algorithm in scheduling the workflow so that the cost was reduced by up to 100% in some cases, and the algorithm proved its superiority over competing algorithms.
Key words: hybrid cloud, genetic algorithm, heuristic algorithm, cost, time, workflow
up
|
| |
Reference
1- AR. Arunarani, D. Manjula, Vijayan Sugumaran. 2019.Task scheduling techniques in cloud computing: A literature survey. Future Generation Computer Systems.
2- B P Abbott et al. 2009. LIGO: the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory. REPORTS ON PROGRESS IN PHYSICS.
3- El-Mihoub TA, Hopgood AA, Lars N, Battersby A. 2006. Hybrid genetic algorithms: A review. Eng Lett
4- Flexera “State of the Cloud Report 2021”, https://info.flexera.com/CM-REPORT-State-of-the-Cloud?lead_source=Website%20Visitor&id=Flexera.com-PR#download.
5- Iranmanesh Amir, Naji Hamid Reza. 2021. DCHG-TS: a deadline-constrained and cost-effective hybrid genetic algorithm for scientific workflow scheduling in cloud computing. Cluster Comput
6- Junlong Zhou, Tian Wang, Peijin Cong, Pingping Lu, Tongquan Wei, Mingsong Chen. 2019. Cost and makespan-aware workflow scheduling in hybrid clouds. Journal of Systems Architecture.
7-Kumara Sastry, David E.Goldberg. Analysis of Mixing in Genetic Algorithms: A survey. 2003.
Environmental Science.
8- Mohit Kumar , S.C. Sharma , Anubhav Goel , S.P. Singh. 2019. A comprehensive survey for scheduling techniques in cloud computing. Journal of Network and Computer Applications .
9- M. Manasrah Ahmad, Ba Ali Hanan. 2018. Workflow Scheduling Using Hybrid GA-PSO Algorithm in Cloud Computing. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing
10- Raja Manish Singh, et al. 2014. Task Scheduling in Cloud Computing: Review. International Journal of Computer Science and Information Technologies 5 (6).
11- Rassoul Khosravanian, Vahid Mansouri, David A. Wood, Masood Reza Alipour. 2018. A comparative study of several metaheuristic algorithms for optimizing complex 3‑D well‑path designs. Journal of Petroleum Exploration and Production Technology.
12- Samadi Yassir, Zbakh Mostapha, Tadonki Claude. 2018. E-HEFT: Enhancement Heterogeneous Earliest Finish Time algorithm for Task Scheduling based on Load Balancing in Cloud Computing. International Conference on High Performance Computing & Simulation.
13- Sukhpal Singh , Inderveer Chana. A Survey on Resource Scheduling in Cloud Computing: Issues and Challenges. 2016. J Grid Computing.
14- Topcuoglu Haluk, Hariri Salim, Wu Min-you. 2002. Performance-effective and low-complexity task scheduling for heterogeneous computing. IEEE transactions in parallel and distributed systems.
up
|
| |
النتائج:
نستعرض فيما يلي نتائج تنفيذ الخوارزميات والسيناريوهات المنفذة والمشروحة سابقاً موضحين قيم وسيطات Parameters البحث الرئيسية وهي: الكلفة وقيد زمن التنفيذ.
أولاً: الكلفة الناتجة عن استئجار موارد السحابة العامة:
يوضح الشكلين (4)، (5) كلفة استئجار موارد السحابة العامة، نلاحظ بشكل واضح أن كلفة استئجار الموارد تنخفض في خوارزمية HGTH، عند استخدام نفس العدد من الآلات الافتراضية الخاصة المستخدمة في خوارزمية DCOH والتي بلغ عددها عشر آلات وتنفيذها على سير العمل INSPIRAL في الحالات المختلفة الموضحة مسبقا فإن الخوارزمية حققت تحسين واضح قارب 99%، وكلما ازداد حد الزمن المعطى كلما كانت النتائج أفضل وخاصة في الحالات التي يكون فيها عدد المهام قليل نسبياً.
العدد القليل للآلات الافتراضية الخاصة يجعل كلتا الخوارزميتين تستخدمان السحابة العامة، وكذلك الأمر عند تزايد عدد العقد في سير العمل، حيث لا تكفي الآلات الخاصة لتنفيذ كامل سير العمل، فيتم اللجوء للسحابة العامة، لكن استراتيجية خوارزمية HGTH لها أفضلية بسبب إعطائها أولوية للآلات الافتراضية الخاصة على العامة، وكذلك تفضيل الآلات الافتراضية العامة ذات الكلفة الأقل، في مرحلة التوزيع الأولي للموارد وفق خوارزمية E-HEFT.
ثانياً: حد الزمن
يوضح الشكلين (6)، (7) حد الزمن النهائي للتنفيذ الذي تم توضيحه في الجدول (4)، لنلاحظ أن كلا الخوارزميتين تتقيدان بحد الزمن مع اختلاف بسيط في زمن تنفيذ سير العمل الكلي، وهذا التقارب مناسب طالما تم تخفيض الكلفة والالتزام بقيد الزمن تكون الخوارزمية قد حققت المطلوب.
تبين الأشكال أن خوارزمية HGTH تقترب من حد الزمن بشكل أكبر من خوارزمية DCOH، وذلك مقبول طالما تحقق الخوارزمية حد الزمن ولا تتجاوزه وفق شرط تابع اللياقة الموضوع فيها، بسبب التركيز الأكبر على تخفيض كلف تنفيذ سير العمل.
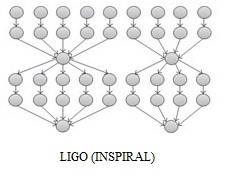
الشكل (3)[9]
سير العمل Inspiral
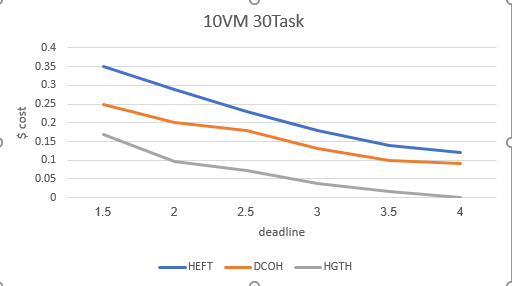
الشكل (4)
Cost Inspiral30
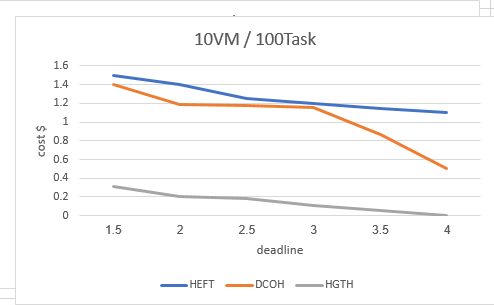
الشكل (5)
Cost Inspiral100
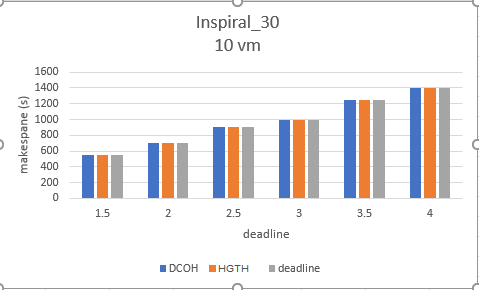
الشكل (6) Deadline Inspiral 30
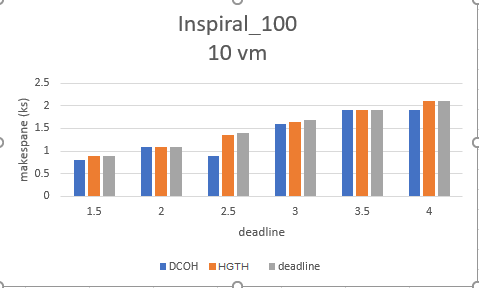
الشكل (7) Deadline Inspiral100
|